Types of photovoltaic systems
|
|
The
stand
alone![]() photovoltaic
systems
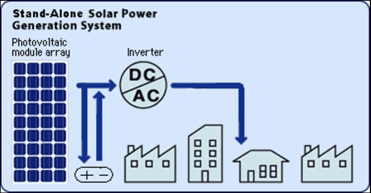
photovoltaic
systems![]() are
used mainly in isolated areas where it is not possible to connect to the
electricity network. With this type of system, energy storage is guaranteed by
batteries
are
used mainly in isolated areas where it is not possible to connect to the
electricity network. With this type of system, energy storage is guaranteed by
batteries![]() , with the
possibility of having a direct current voltage of 12, 24, 48 V and, thanks to
inverters
, with the
possibility of having a direct current voltage of 12, 24, 48 V and, thanks to
inverters![]() , an
alternate current of 110, 220, 400 V (Fig. 1).
, an
alternate current of 110, 220, 400 V (Fig. 1).
The system must be
overdimensioned in order to be able to supply
energy even in bad weather or during winter months.
Only
certain special systems can supply
energy directly during the night too.
|
|
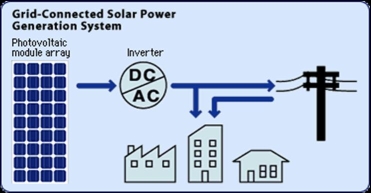
The grid
connected![]() photovoltaic systems (Fig. 2) are
attached to the electricity network and act as producers and/or consumers of
electric energy: when the domestic (or industrial) system overproduces energy
(i.e. when it manages to cover its own needs), the excess is passed on to the
electricity company. It is introduced into the network and counted with a "debit"
meter by the electricity company.
photovoltaic systems (Fig. 2) are
attached to the electricity network and act as producers and/or consumers of
electric energy: when the domestic (or industrial) system overproduces energy
(i.e. when it manages to cover its own needs), the excess is passed on to the
electricity company. It is introduced into the network and counted with a "debit"
meter by the electricity company.
If the system does not manage to cover its electric energy needs, for example during the night, the energy for the consumers is taken from the electricity network with a "credit" meter.
The
Law of 28 July 2005 (Criteria for offering incentives for the production of electric
energy by means of a "photovoltaic convention") states that for small systems of
less than 20
kWpeak![]() the electric energy sent to the network is paid for, over a 20-year period, at 0.445 Euros/kWh
the electric energy sent to the network is paid for, over a 20-year period, at 0.445 Euros/kWh![]() (while that taken from the network is paid for at approximately 0.15 Euros/kWh).
(while that taken from the network is paid for at approximately 0.15 Euros/kWh).
The Webweavers: Last modified Wed, 1 Dec 2006 10:23:30 GMT