Energy. Electric energy
 |
|
|
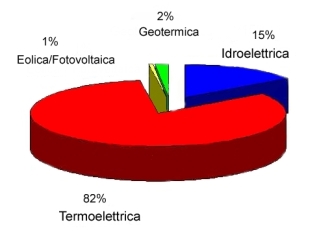
Fig. 1: Sources used for production of electric energy in Italy in 2003. Credit: (GRTN S.p.A) |
The energy problem is one of mankind’s most pressing problems today, and Scienzagiovane will be taking a detailed look at it over the next few months.
In this article we will discuss electric energy![]() ,
solar energy
,
solar energy![]() and in particular photovoltaic roofs, their characteristics, their
efficiency
and in particular photovoltaic roofs, their characteristics, their
efficiency![]() and their future.
and their future.
Electric energy![]() is an intermediate form of energy. It is produced in
thermal power stations
(where fuel oil
is an intermediate form of energy. It is produced in
thermal power stations
(where fuel oil![]() ,
gas
,
gas![]() , coal,
biomass
, coal,
biomass![]() , etc. are burnt),), in hydroelectric power stations and nuclear power stations;
smaller quantities are produced by wind, photovoltaic solar panels, sea
tides, etc. (Fig. 1).
, etc. are burnt),), in hydroelectric power stations and nuclear power stations;
smaller quantities are produced by wind, photovoltaic solar panels, sea
tides, etc. (Fig. 1).
Electric energy is easily transportable via integrated electric grids. After transportation, electric energy is converted into mechanical energy, thermal energy, light energy, chemical energy, etc.
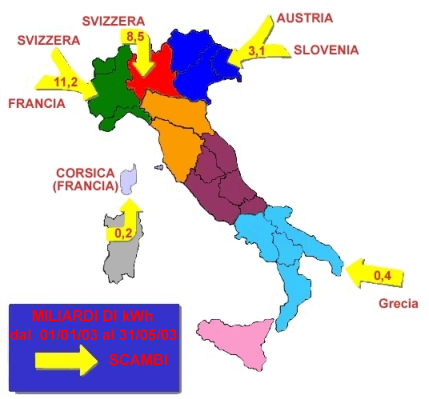 Fig. 2: Imports of electric energy in Italy in 2003. Credit: (GRTN S.p.A) |
Italy mainly produces electric energy with fossil fuel
thermal power stations![]() (using methane
(using methane![]() ,
fuel oil and coal), in
hydroelectric
,
fuel oil and coal), in
hydroelectric![]() power stations and in geothermal
power stations and in geothermal![]() power stations (Fig.1), and is the European country which imports the most electric energy,
in particular from France, Switzerland, Austria and Slovenia. (from
nuclear power stations
power stations (Fig.1), and is the European country which imports the most electric energy,
in particular from France, Switzerland, Austria and Slovenia. (from
nuclear power stations![]() )
(Fig. 2).
)
(Fig. 2).
It is predicted that in the coming decades the demand for electric energy worldwide will have its highest rate of growth ever: consumption should double in the next 10 to 20 years.
Electric energy must be produced at the moment of demand and this leads to the particular problem of meeting demand at peak times – in Italy these are from 8.30 to 11.30 am and from 4 to 7 pm. During the summer, demand increases also around 2 pm with the switching on of air conditioning systems, now used much more frequently than in the past. During these hours, all the available electric power stations are put into operation.
To avoid the possibility
of a black-out, there is an urgent need to improve the distribution network and increase
the production capacity of electric energy. On the other hand, Italy must gradually
reduce emissions into the atmosphere of
greenhouse gases![]() , basically
CO2
, basically
CO2![]() ,
in accordance with the commitments made in the Kyoto agreement.
This would require a prudent saving of energy and a greater use of non-polluting sources of energy.
One example could be the use of solar energy, exploiting
photovoltaic
,
in accordance with the commitments made in the Kyoto agreement.
This would require a prudent saving of energy and a greater use of non-polluting sources of energy.
One example could be the use of solar energy, exploiting
photovoltaic![]() technology.
technology.
The ENEA project “10000 photovoltaic roofs”, and its extension to include a much greater number, is concerns the installation of photovoltaic panels on the roofs of public buildings and private houses using state, regional and local subsidies and EEC funds. This initiative is certainly a positive way of encouraging a more widespread exploitation of solar energy; it must be said, however, that it has not always worked. In fact, in some cases the users only cared about keeping the panels just long enough to recover the portion of initial costs which they themselves had met.
For this reason the incentive was recently modified; it is transferred into
the electric energy produced. Sent to the electric grid, at the moment, photovoltaic electric energy is still not
economically competitive compared to electric energy from
fossil fuels![]() ,
nuclear reactory and wind farms.
,
nuclear reactory and wind farms.