Luigi Galvani (continued)
|
|
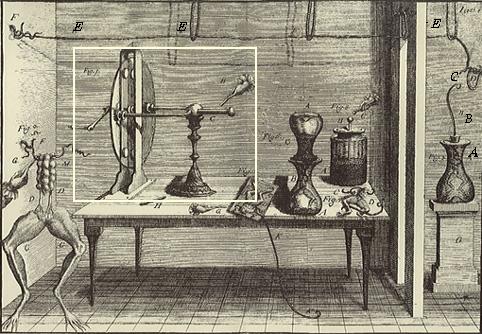
| Fig. 3:
Illustration of the experiment
showing the excitation at a distance of the crural nerve of a frog as the
effect of a spark released by the conductor of an electrostatic generator.
The conductor, as well as the stick carrying the conductor employed to
extract the spark from the machine, can be seen on the left. Note the metallic cable E drawn across the room
- it is isolated by letting it hang from silk knots: at one of the ends was
hanging the hook B, communicating through a metallic wire with the crural
nerves of a frog, kept in the glass container A. The frog's legs were in
contact with a conducting material, in this case lead shot.
(Credit: Dall'opera "De viribus electricitatis in motu musculari commentarius") |
The experimental set-up used by Galvani in these experiments closely resembles modern radio-telegraphic transmitting-receiving apparatus: the discharges produced by the machine are generically oscillating; they generated radio waves that, propagating, generated in turn high frequency currents in the wire E, which worked as the antenna of the receiving apparatus. The crural nerves of the frog operated as a detector, the lead shot as ground. The interpretation of the experiments in these terms is, however, recent: before the theoretical and experimental studies carried out by Maxwell and Hertz towards the end of the twentieth century, it could not make its way either in the mind of Galvani or in that of those who learned about them.
In those days it was not generally agreed that "artificial electricity" – that produced and studied in a laboratory – and atmospheric electricity, which manifests itself, for instance, in terms of flashes of lightning, were of the same nature. "After arriving at the discoveries expounded until now regarding the force of artificial electricity in muscular contractions – wrote Galvani – it was our wish to investigate if the so-called atmospheric electricity could produce, or not, the same phenomena: that to say, whether, following the same devices, the discharge of lightning would produce muscular contractions like those produced by the spark". He carried out some experiments to reveal the possible effects.
|
|