Who are the favourite targets?
There is such a huge number
of different mechanisms and instruments involved in computer piracy that it is impossible to mention and
describe all of them; vulnerabilities are lurking at all levels, in
application programmes![]() , in
operating systems
, in
operating systems![]() and in the way the network works. However, in order to be able to exploit
these weaknesses, you must have a relatively sophisticated knowledge of computers.
and in the way the network works. However, in order to be able to exploit
these weaknesses, you must have a relatively sophisticated knowledge of computers.
A cyber attack on a computer system usually
consists of various phases: it often starts with what we might call a "geographic reconnaissance"
of the local network (LAN
![]() ), i.e. the
network
), i.e. the
network![]() around the target is checked out or, to use the jargon,
the "network is scanned". The aim is to establish which computers and network apparatus are active,
collect information and try to determine with special programmes ("software probes") which operating systems
are present and what their weaknesses are. Then, using other programmes which exploit these vulnerabilities,
the hacker forces his way into the targeted systems and manipulates them in order to gain full control
For example, he can get as far as acquiring administrator privileges, or deciphering user passwords. As with
all illegal activities, he then tries to cover the traces inevitably left by his intrusion.
around the target is checked out or, to use the jargon,
the "network is scanned". The aim is to establish which computers and network apparatus are active,
collect information and try to determine with special programmes ("software probes") which operating systems
are present and what their weaknesses are. Then, using other programmes which exploit these vulnerabilities,
the hacker forces his way into the targeted systems and manipulates them in order to gain full control
For example, he can get as far as acquiring administrator privileges, or deciphering user passwords. As with
all illegal activities, he then tries to cover the traces inevitably left by his intrusion.
At this point, the hacker
can launch attacks on the specific system, or he can intercept, cancel or
manipulate data and programmes. Either "
sniffer![]() " or "
backdoor
" or "
backdoor![]() " can be installed: the former are programmes which intercept data transmitted on the network, the latter allow future access to the
computer even if the intrusion is discovered.
" can be installed: the former are programmes which intercept data transmitted on the network, the latter allow future access to the
computer even if the intrusion is discovered.
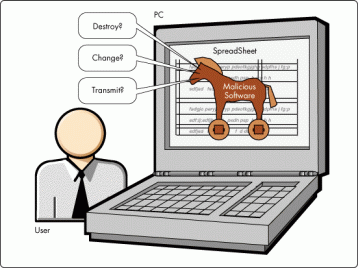 |
Fig. 1:
Possible actions of a Trojan horse. (Credit: New Threats: Paranoia Becoming Reality) |
Amongst the instruments at the hacker's disposal are the so-called
"Trojan horses". These are programmes which carry out particular operations but which also contain hidden functions which are carried out unbeknown to the user. For example, a programme which manages a
database![]() , besides acting as a normal database, could reveal the entire contents of the hard disk to unauthorized users, with obvious consequences. There is a lesson to be learnt here: never install software that comes from strangers or whose origins are not known, even if it comes from friends – they too could have been subjected to intrusions.
, besides acting as a normal database, could reveal the entire contents of the hard disk to unauthorized users, with obvious consequences. There is a lesson to be learnt here: never install software that comes from strangers or whose origins are not known, even if it comes from friends – they too could have been subjected to intrusions.
The techniques for attacking computers are getting more and more sophisticated and are under continuous development. In some cases software agents are used which can propagate autonomously on Internet and spread all over the world. "Bot" (short for robot) software can be spread on Internet and, by communicating with each other, they can control hundreds of computers which are then compromised with backdoors (access entry points unknown to the system administrator) and can be used to launch coordinated attacks against chosen targets.
For example, in February 2000, thanks to a particularly sophisticated attack of "Distributed Denial of Service" (DDoS![]() ) lots of important companies which used the network for business purposes (e-commerce) were blocked for several hours because their web sites were interrupted, leading to considerable financial losses. The DDoS is a technique by which hundreds of computers are used to launch a coordinated and simultaneous attack on a target. This means involving a large number of agents (computers which execute the attack directly), not to mention
a certain number of masters to coordinate them - masters who are in turn guided by the attacker's computer (see Fig.2).
) lots of important companies which used the network for business purposes (e-commerce) were blocked for several hours because their web sites were interrupted, leading to considerable financial losses. The DDoS is a technique by which hundreds of computers are used to launch a coordinated and simultaneous attack on a target. This means involving a large number of agents (computers which execute the attack directly), not to mention
a certain number of masters to coordinate them - masters who are in turn guided by the attacker's computer (see Fig.2).
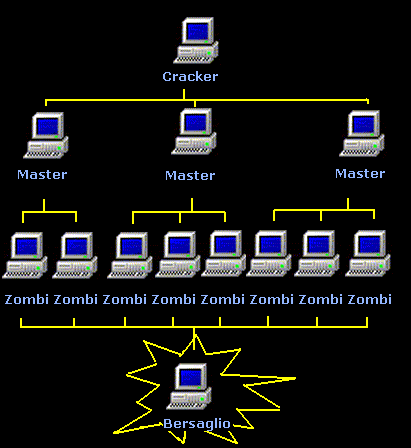 |
Fig. 2: "Distributed Denial of Service" (DdoS) attacking technique. The attacker (Cracker) inserts a certain number of agents (masters) which in turn guide the attack of the
"Zombies" against the target. (Credit: B. Poli – Physics Dept., University of Bologna) |
Unfortunately, the techniques are not always so complex. In the simpler cases, thanks to a well-known weakness (well-known in hacker circles, obviously), files containing programmes are copied onto the target computer. When these programmes are activated they can perform various tasks, e.g. create illegal accesses (backdoors), activate hidden connections, probe files, etc, depending on the particular interests of the hacker.
Nowadays you do not need to be a computer expert to be able to gain illegal access to a computer; you can simply use "ready-made" programmes available on line, which exploit well-known vulnerabilities. Computer piracy also uses what is called in jargon "social engineering", a form of attack on a computer through its user, who is sometimes more defenceless than the computer itself. By pretending to be a system administrator, a new collaborator or a potential client, they use the phone, e-mail or fax to ask for specific technical details such as a password, modem telephone numbers for access from outside, programmes used or network configurations. These techniques exploit the good faith of the user, just like in other all too frequent cases of fraud in our society. Computer piracy operates through the human psyche too!