Stars too are born and die
In the past, stars was considered immutable; only in the XX century was
it undestood that stars are born and die, but their life is much longer than human life: the Sun may live about ten billion years.
Stars originate from a slow gravitational collapse in an interstellar gas and dust cloud![]() (Fig. 1) with molecular hydrogen and helium.
The potential energy lost in the collapse is transformed in thermal energy.
When the central part of the cloud reaches a temperature of 2000 oK,
the hydrogen molecules break into atoms. After that, the central
temperature continues to increase).
(Fig. 1) with molecular hydrogen and helium.
The potential energy lost in the collapse is transformed in thermal energy.
When the central part of the cloud reaches a temperature of 2000 oK,
the hydrogen molecules break into atoms. After that, the central
temperature continues to increase).
 |
Fig. 1: A spectacular image of the center of an "Omega Nebula", called M 17; this nebula is 5000 light years (Credit: Photo NASA, ESA 24/04/2003) |
When the central temperature is greater than half a milion oK,
thermonuclear fusion starts and a protostellar object is born that emits mainly infrared radiation![]() .
.
The destiny of a star depends on its initial mass:
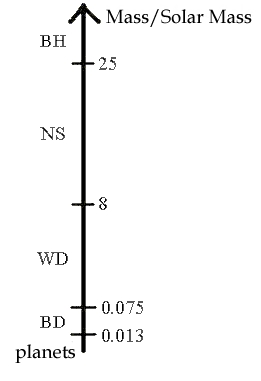 |
- If the mass is less than 0.013 solar mass
 no thermonuclear reactions start and a planet is produced.
no thermonuclear reactions start and a planet is produced.
- If the mass is between 0,013 and 0,075 solar mass
 in the core there is a temperature of 1 million Kelvin degrees, the first thermonuclear reactions start but
this is not enough to have a steady hydrogen burning: we obtain a brown dwarfs
in the core there is a temperature of 1 million Kelvin degrees, the first thermonuclear reactions start but
this is not enough to have a steady hydrogen burning: we obtain a brown dwarfs  (BD).
(BD).
- Between 0,075 and 8 solar mass
 a normal star, like our Sun, is produced; after an initial phase of some billions
of years there is the formation of a planetary nebula
a normal star, like our Sun, is produced; after an initial phase of some billions
of years there is the formation of a planetary nebula phase with a strong mass loss. The stars become white dwarfs
phase with a strong mass loss. The stars become white dwarfs (WD), like the
nebula Helix central star (Fig. 2); if the mass of these stars is between 0.075 and 0.4 solar mass they are called
red dwarfs
(WD), like the
nebula Helix central star (Fig. 2); if the mass of these stars is between 0.075 and 0.4 solar mass they are called
red dwarfs and have a very long life, but this is not a final stage of a star's life.
and have a very long life, but this is not a final stage of a star's life.
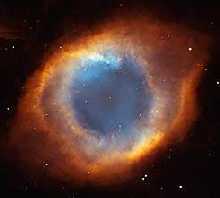
Fig. 2: The Nebula Helix image taken by the Hubble Space Telescope  . The central small star is the white dwarf.
. The central small star is the white dwarf.
(Credit: Photo NASA, ESA, STscI) - Stars heavier than 8 solar mass
 explode like a type II supernovae SN II
explode like a type II supernovae SN II ; they emit a cloud and the core becomes a neutron star
; they emit a cloud and the core becomes a neutron star (NS) if its initial mass is less than 25 solar mass.
(NS) if its initial mass is less than 25 solar mass.
- Above this mass value (not a sure value) a stellar black hole
 (BH) derives from the SN II
explosion.
(BH) derives from the SN II
explosion.