Neuropsychiatric disorders
These are diseases that
profoundly, and often irreversibly, alter the behavior and intellectual ability
of patients, sometimes in the absence of patent neurodegenerative
alterations![]() .
Today, some of them can be revealed through non invasive brain imaging
techniques. The most frequent and devastating of these diseases is
schizophrenia
.
Today, some of them can be revealed through non invasive brain imaging
techniques. The most frequent and devastating of these diseases is
schizophrenia![]() whose symptoms are dramatic alterations of personality, acoustic and visual
hallucinations, construction of false beliefs, hyperactivity, aggressive
behavior or social isolation with apathy, persecution complex and tendency
towards suicide. In addition to altered behavior, the diagnosis of schizophrenia
can be confirmed by brain-imaging techniques that usually reveal an abnormal
enlargement of the
ventricles
whose symptoms are dramatic alterations of personality, acoustic and visual
hallucinations, construction of false beliefs, hyperactivity, aggressive
behavior or social isolation with apathy, persecution complex and tendency
towards suicide. In addition to altered behavior, the diagnosis of schizophrenia
can be confirmed by brain-imaging techniques that usually reveal an abnormal
enlargement of the
ventricles![]() (Fg.1).
(Fg.1).
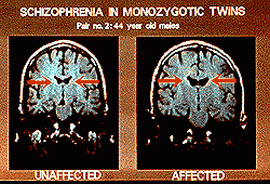 |
Fig. 1:
MRI (Credit: NIMH (National Institute of Mental Health) Clinical Brain Disorders Branch) |
Different types of depressions
or of manic-depressive syndromes affect about 1% of people. These diseases may
result not only in serious medical problems, but also in relevant problems from
the social and economic point of view. In the most serious cases, indeed,
symptoms similar to those of schizophrenia may become manifest, with patients
presenting impaired working ability and social relationships. Non-invasive brain
imaging techniques may help medical treatment in these cases too. In Fig. 2, for
instance, brain areas stained in yellow to red point at areas having the largest
cerebral activity and it is easy to see that they are substantially reduced in
the brain of a depressed patient. Schizophrenia and major depressive diseases
are linked to the altered activity of specific
neurotransmitters![]() in various
brain areas. A large spectrum of anti-psychotic drugs are presently available
for the treatment of these diseases. These drugs, whose main effect is the
control of disease symptoms, must be used under strict medical control.
in various
brain areas. A large spectrum of anti-psychotic drugs are presently available
for the treatment of these diseases. These drugs, whose main effect is the
control of disease symptoms, must be used under strict medical control.
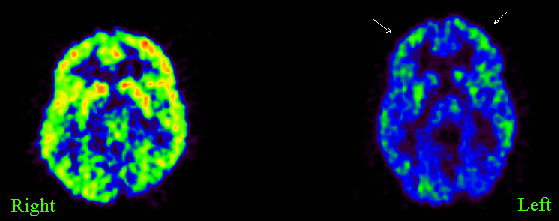
Fig. 2: PET![]() brain imaging:
comparison between the brain of a depressed patient (right) and a normal
control (left).
brain imaging:
comparison between the brain of a depressed patient (right) and a normal
control (left).
(Credit:
Medical
University of South Carolina (MUSC) - Center for Advanced Imaging Research (CAIR))